Choosing the right mobile screen is essential to your smartphone experience. Whether you’re a movie buff, gamer, or someone who enjoys vibrant colors, understanding mobile display types can help you decide.
This guide will break down the three main types of displays—OLED, LED, and LCD. We’ll explore their features, pros and cons, and the devices that use them.
OLED Displays
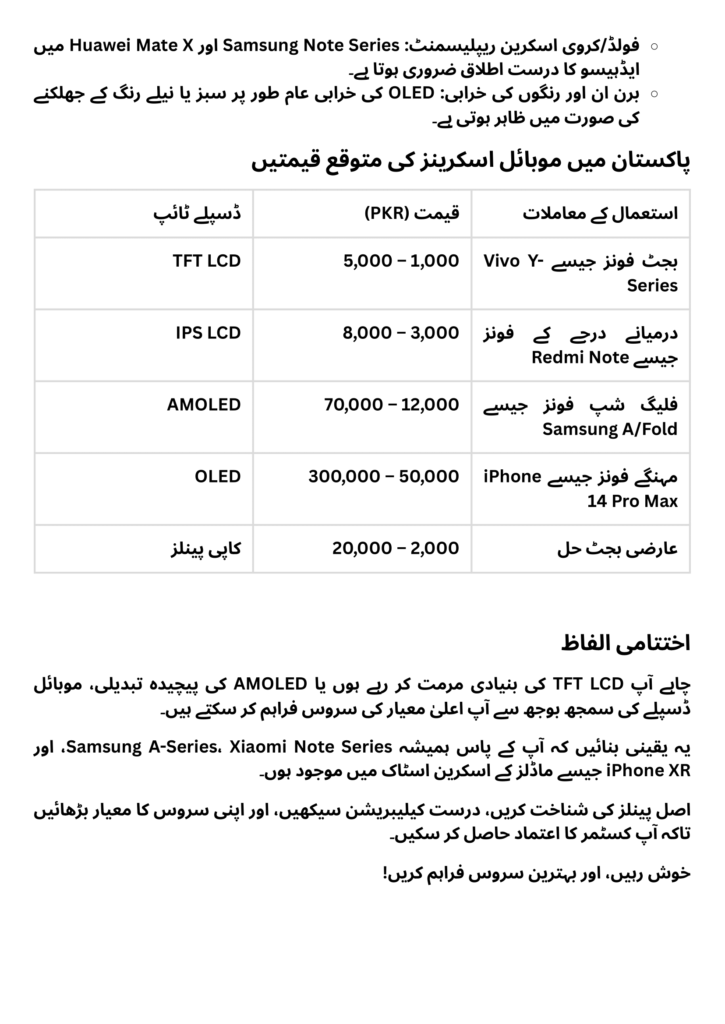
OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) displays are famous for their vibrant colors, deep blacks, and sleek designs. They stand out due to their self-emissive pixels, meaning each pixel produces its own light, eliminating the need for a backlight.
Features
- Self-Emitting Pixels: Individual pixels emit light, enabling true blacks by switching off completely.
- Slim Design: Thinner and more flexible, perfect for curved and foldable devices.
- Premium Quality: OLED screens deliver unmatched contrast, vibrant colors, and smooth performance.
- Durability: Built with heat-resistant copper paper on the back.
- Materials: Made from flexible papers like reflective and heat-resistant materials.
Advantages
- Exceptional color accuracy and contrasts.
- Energy-efficient in dark modes.
- Ideal for immersive viewing experiences.
Disadvantages
- Expensive, with costs ranging from PKR-20000 to PKR-2Lac.
- May suffer from “burn-in” over long-term usage.
Examples of Devices with OLED Screens
- Samsung Galaxy S20, S21, S22, and Ultra models.
- iPhone X to iPhone 15 Pro Max.
- Google Pixel 3XL to Pixel 9 Pro.
- Huawei Mate 10 Pro, Nova 7, P20 Pro, P30.
OLED is best suited for premium devices and offers the most immersive visual experiences.
LED Displays
LED (Light-Emitting Diode) displays share some similarities with OLED but rely on a backlight to illuminate pixels. They are more affordable than OLED while still delivering excellent performance.
Features
- Backlit Pixels: Unlike OLED, LED pixels are illuminated by a backlight.
- Built-In Features: Combine light, touch, and display functionality.
- Robust Build: Made from durable crystal glass with heat-protective copper or grey-paper backing.
- Dual Strips: Includes two strips–one for display and another for touch control.
Advantages
- Cost-effective, priced between PKR.5000 to PKR.25000.
- Excellent energy efficiency.
- Bright enough for outdoor use and reliable heat dissipation.
Disadvantages
- Lacks OLED-level depth with blacks and color vibrancy.
- Colors often lean toward blue or greenish shades.
Examples of LED Copy Panels
LED also includes various “copy panels” that mimic premium features but operate on lower budgets.
- IC Panel: Marketed as “OLED panels,” but technically LED.
- TFT, OGS, and INCELL Panels: Types of LCDs marketed under LED, suitable for budget-friendly phones.
LED displays are a good middle ground for users wanting decent performance without a high price tag.
LCD Displays
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) is one of the oldest display technologies. While less advanced than OLED or LED, it remains widely popular for its affordability and reliability. LCD uses a backlight to project light through liquid crystals and display content.
Features
- Thick Design: Bulkier compared to OLED and LED screens.
- Non-Built-In Components: Touch and display systems are often separate.
- Replaceable Parts: Backlight is replaceable for extended use.
- Material: Made from standard glass materials.
Advantages
- Budget-friendly, costing around PKR/300 to PKR/5k.
- Durable, with less risk of screen burn-in.
- Jet-black tonal quality.
Disadvantages
- Inferior viewing angles compared to OLED or LED.
- Lower color vibrancy and contrast.
- Single media strip limits functionality compared to dual-strip LED panels.
Examples of LCD Panels
- Commonly found in budget devices and entry-level smartphones.
- Apple iPhone XR and iPhone 11 series still use LCD.
LCD screens cater to those who prioritize cost-effectiveness over high-end features.
Key Differences Between OLED, LED, and LCD
| Feature | OLED | LED | LCD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Backlight | None (Self-illuminating pixels) | Required | Required |
| Design | Ultra-thin and flexible | Slim but rigid | Thick |
| Price Range | PKR/20k to PKR/2L | PKR/5k to PKR/25k | PKR/300 to PKR/5k |
| Color Quality | Deep blacks, vibrant colors | Bright, good for sunlight | Less contrast, jet-black |
| Durability | Can experience burn-in | Longer-lasting in most cases | Durable but lower quality visuals |
| Best Use Case | High-end smartphones | Mid-range devices | Budget-friendly options |
Mobile Display Types Guide for Technicians in Pakistan
Mobile technicians frequently encounter a range of display issues and replacements in their day-to-day work. Whether it’s understanding the differences between display types or diagnosing problems related to TFT panels or AMOLED burns, having detailed knowledge about mobile phone displays is essential. This guide is crafted specifically for technicians in Pakistan, providing technical details, troubleshooting tips, and insights into repairing or replacing displays.
We’ll cover LCD, LED, and OLED technologies, highlighting their subtypes, benefits, challenges, and the steps to handle common issues. Prices for each type are listed in PKR to help with cost estimation during servicing.
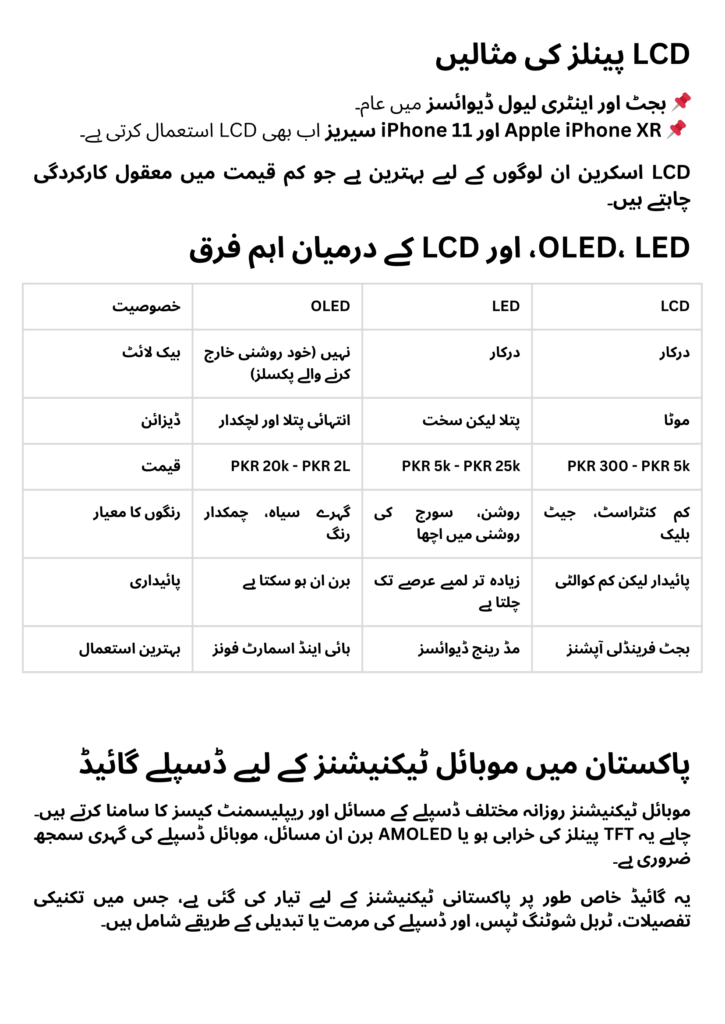
1. LCD (Liquid Crystal Display)
How LCD Works
LCD screens use a backlight system (CCFL or LED) to illuminate the screen from behind. Without this backlight, the display won’t be visible, as the liquid crystals themselves do not emit light. This makes LCD power-hungry compared to newer technologies.
Understanding LCD Types and Repair Complexity
TFT LCD (Thin Film Transistor)
Common in budget models, TFT LCDs provide basic functionality at a low cost. Each pixel connects to a transistor and capacitor, ensuring decent response rates. However, they suffer from poor sunlight visibility and limited viewing angles.
- Identification Tips:
- Thick screen with dimming issues under bright light.
- Check for budget models like Tecno Pop series or Vivo Y-series under 25K PKR.
- Single media strip for basic configuration.
- Common Issues:
- Backlight Failure: Inspect the light sheet and replace if dim.
- Pixel Dead-line Issues: Result from connector damage or IC failure.
- Replacement Tips:
- Replacement panels cost between PKR 1,000–5,000 depending on the device.
- Always confirm backlight quality post-installation.
IPS LCD (In-Plane Switching)
A superior alternative to TFT, IPS LCDs have wider viewing angles and better color reproduction. These are a staple in mid-range devices priced between PKR 20,000–60,000.
- Identification Tips:
- Higher pixel density than TFT; brightness adjusts better to sunlight.
- Common in devices like Xiaomi Redmi Note 12 or Samsung A-series.
- Troubleshooting:
- Flickering Display: Often caused by damaged connectors or low-quality replacements.
- Brightness Unevenness: Points to backlight degradation; check for loose backlighting pins.
- Repair Process:
- IPS screens are delicate; check the adhesive application during installation.
- Replacement costs start from PKR 3,500 for mid-range models upwards to PKR 8,000.
SLCD (Super LCD)
SLCD panels offer reduced gaps between touch sensors and display glass, resulting in better responsiveness. These were previously popular in older HTC or budget Samsung devices.
- Challenges While Repairing:
- Limited availability of replacement units. Ensure compatibility for older models.
- Check for factory-calibrated adhesive seals during installation to avoid parallax errors.
2. LED (Light-Emitting Diode)
LED technology adds efficiency and brightness, replacing CCFL backlights with tiny LED diodes. This category includes AMOLED and Super AMOLED, often seen in mid-to-flagship devices.
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode)
AMOLED relies on self-emissive pixels, meaning each pixel has its own light source. This technology results in true black levels and power savings because pixels turn off completely when displaying black. Devices under Samsung, OnePlus, or Vivo flagship models widely use AMOLED.
- Issues Diagnosis:
- Dead Pixels: Check individual pixel functionality; dead-diodes often lead to black spots.
- Screen Burn-in: Identified as permanent shadows on static areas (e.g., navigation bars). A diagnostic screen test will reveal these defects.
- Replacement Costs in Pakistan:
- General AMOLED screens start at PKR 12,000 for mid-range models like Samsung Galaxy M-series and go beyond PKR 70,000 for premium models like S-series or Foldables.
- Always confirm the source of AMOLED panels; counterfeit units lack color reproduction consistency.
- Practical Repair Tips:
- Take precautions against moisture infiltration as AMOLED panels are susceptible to water damage. Apply liquid-sealing adhesive when reassembling phones.
- Perform brightness calibration post installation to ensure color accuracy.
Super AMOLED
Super AMOLED eliminates the gap between the touch sensor and display glass, ensuring better sunlight visibility and thinner profiles. These are standard in Samsung Galaxy S-series and Note devices.
- Unique Requirements:
- Ensure thermal paste application behind displays during repair to mitigate heat dissipation issues.
- OEM panels are necessary for S-series due to fingerprint sensor compatibility. Damaged third-party replacements can lead to sensor malfunction.
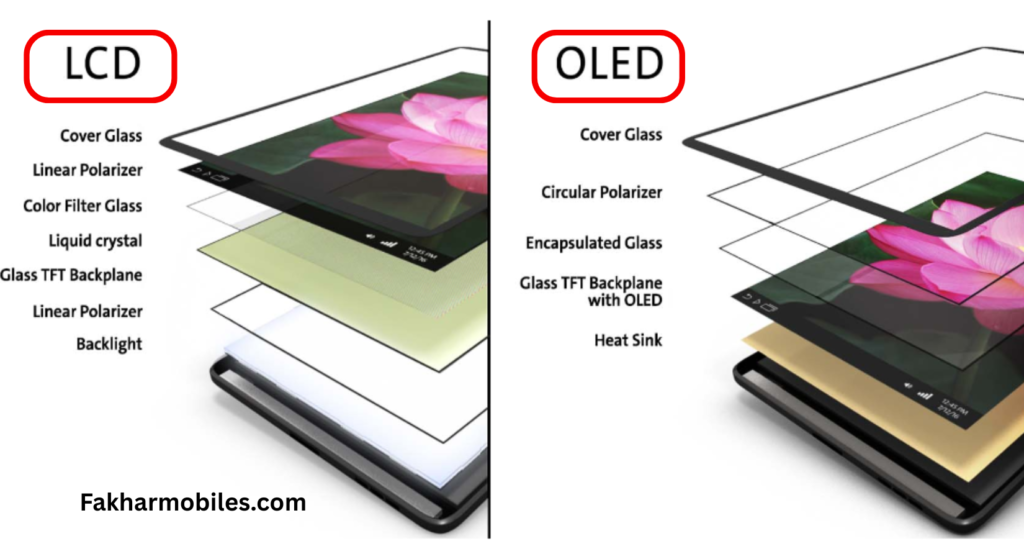
3. OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode)
OLED is similar to AMOLED but doesn’t incorporate the Active Matrix layer. It uses an organic compound film between two conductors to emit light when current passes through. Known for their durability and flexibility, OLEDs dominate premium brands like LG and Apple.
Where OLED Shines
- Durable for premium devices like Huawei Mate Pro and iPhone 14 Pro Max.
- Water-sensitive backlight assembly; proper sealing is necessary during repairs.
Troubleshooting Common OLED Issues
- Edge Screen Replacement (Fold/Curves):
- Curved OLED panels, such as those in Samsung Note series or Huawei Mate X, require precise adhesive application to align the screen.
- Replacement costs start at PKR 50,000–300,000, making it vital to invest in genuine screens.
- Color Tinting:
- Greenish or bluish hue is often caused by degraded diodes. A testing tool can determine the extent.
- Burn-in Mitigation:
- Employ apps that shuffle screen content regularly to avoid static image burns.
- Water Damage Management:
- Devices with OLEDs are less water-resistant post repair unless properly resealed. Check drains and gaskets for tightness after assembly.
Additional Tips for Technicians
1. Identifying Copy Panels
Copy panels are rampant in markets and include options like TFT, PLS, or IN-CELL screens. These are cheaper alternatives but affect touch sensitivity and brightness quality.
- Common Features of Copy Panels:
- TFT screens lack true black visibility and are much thicker.
- Copy OLED variants might lack heat-sink layers, causing overheating.
- Prices for copy panels range between PKR 2,000–20,000, depending on type and compatibility.
2. Handling High-End Displays
- For iPhones from iPhone X onwards (which use OLED), prioritize original refurnished panels. Non-original replacements lack Touch ID calibration and result in sub-par performance.
- High-current brands like Pixel 7 Pro or OnePlus 11 demand original OLEDs due to the heat constraints; allow breaks during benchmark testing post-repair.
3. Testing Tools to Use
- Use multimeter-based pin assessments to inspect faulty ICs related to backlight issues.
- Always rely on diagnostic software to check pixel alignment and uniformity post-installation.
4. Best Practices for Seamless Repairs
- During AMOLED repair, install copper heat sinks (heatsink paper) to diffuse heat efficiently.
- Perform proper gap checks to ensure moisture doesn’t seep into the edges of curved screens.
- For single-strip LCD panels, ensure media ribbons are tightly affixed.

Estimated Costs for Replacements in Pakistan
| Display Type | Price Range (PKR) | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| TFT LCD | 1,000–5,000 | Budget phones like Vivo Y-series. |
| IPS LCD | 3,000–8,000 | Mid-range phones like Redmi Note. |
| AMOLED | 12,000–70,000 | Mid and high-end (Samsung A/Fold). |
| OLED | 50,000–300,000 | Flagship phones (S24 Ultra, iPhone). |
| Copy Panels | 2,000–20,000 | Temporary budget fixes. |
Final Thoughts
From basic TFT repairs to handling complex AMOLED replacements, understanding mobile displays helps technicians provide quick, reliable, and high-quality services.
Keep stock aligned with frequently sought-after models like Samsung A-series, Xiaomi Note series, and iPhone XR. Invest in testing equipment to ensure your service quality mirrors OEM standards. Identifying genuine panels and learning calibration ensures your work stands out and earns customer trust.
Happy Repairing!